Using Water to
Produce Electricity
Vocabulary
Read the vocabulary terms to understand the reading better.
Electricity
Electricity is a form of energy that has positive and negative forms that occur naturally (such as in lightning) or can be produced (such as in a generator) and is the result of electrons moving and interacting together.
Hydroelectric
Hydroelectric means of or relating to producing energy through the use of fast-moving water.
Power Plant
A power plant is groups of buildings, equipment, and machinery that are used to generate electricity from another source of energy such as a hydroelectric dam.
Reservoir
A reservoir is a natural or human-made pond or lake that is used for the storage of water.
Transformer
A transformer is a device that is used to transfer electrical energy from one circuit to another.
Turbine
A turbine is an engine that rotates to produce electricity through the movement of water, air, or steam.
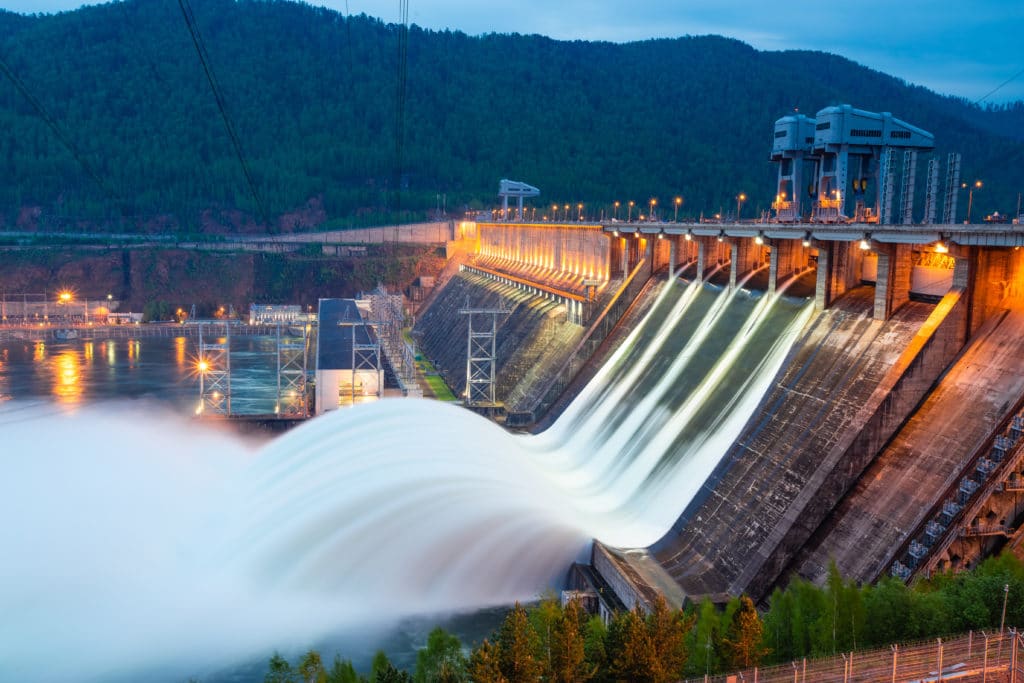
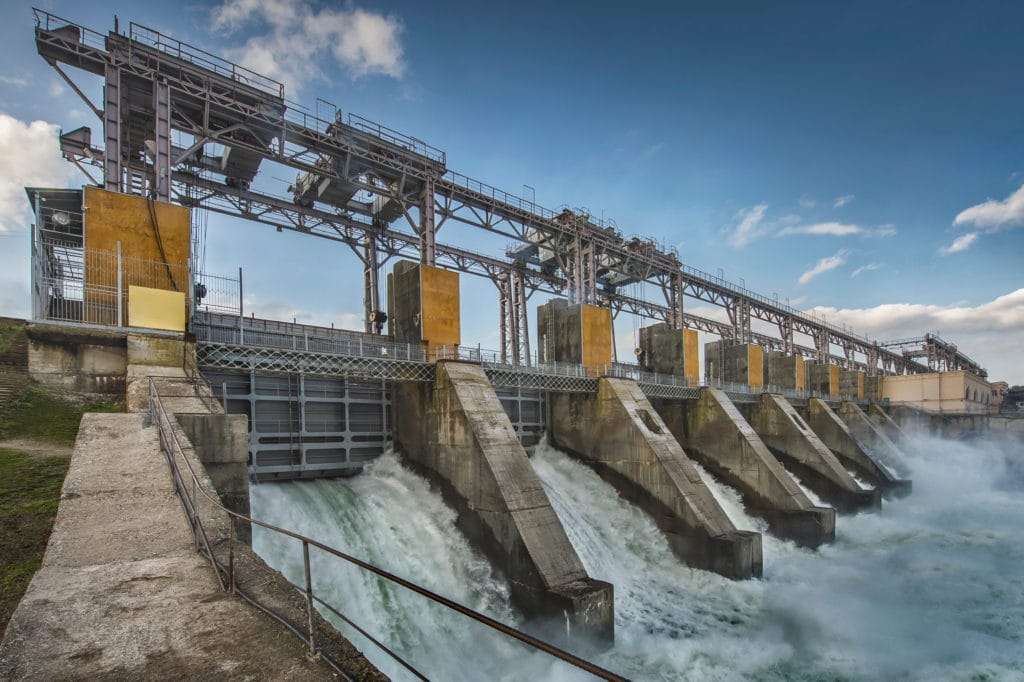
Hydro means “water.” Hydroelectric power plants use water to create electricity.
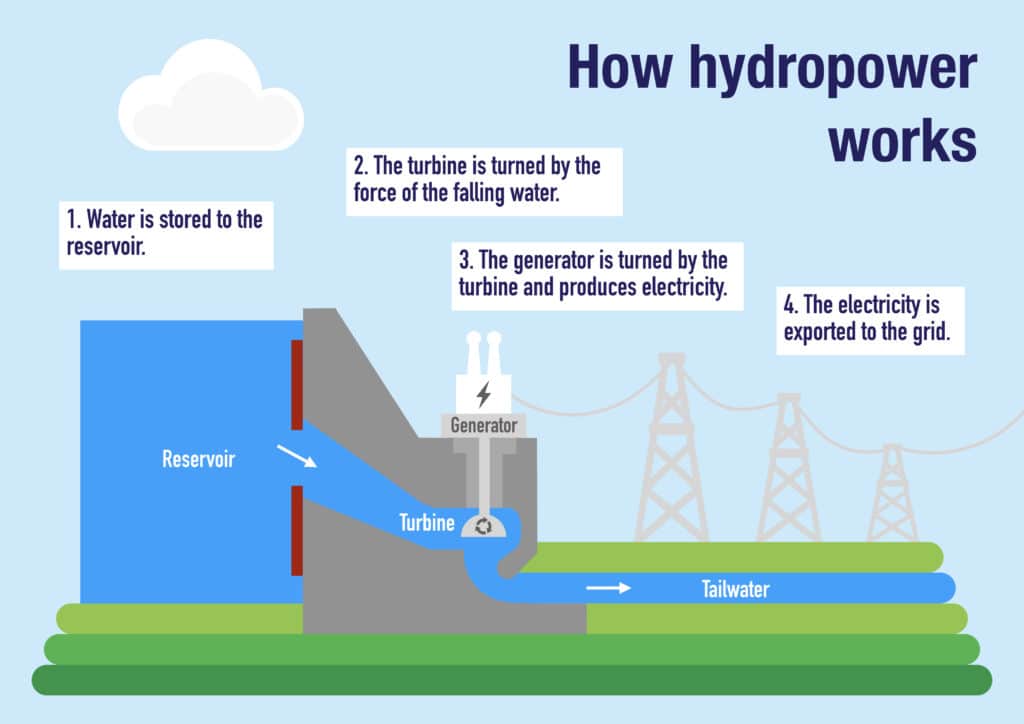
How It Works
- A dam is built in a river. Water collects behind the dam, creating a lake or reservoir.
- When the gates are open, water rushes down a pipe to the turbines.
- The water turns the turbine blades, which turns the rod the blades are attached to.
- The turbine makes the rod and magnets spin very quickly inside the generator.As the magnets spin, charge builds up in coils of copper wire, creating electricity.
- The electricity travels along wires to the transformer. The transformer can help send electricity far away to where electrical power is needed.


To learn more about hydroelectricity, watch the video by Student Energy on YouTube.
Show What You Know!
Complete some questions about the reading selection by clicking “Begin Questions” below.