Forces and Structures
Vocabulary
Read the vocabulary terms to understand the reading better.
Dead Loads
Dead loads are permanent forces acting on a structure or anything that is permanently attached to a structure, such as the weight of the roof attached to a house.
External Forces
External forces are forces that act on a system from the outside.
Internal Forces
Internal forces are forces that are created by the external forces acting on parts of a structure such as poles, roofs, or columns.
Live Loads
Live loads are temporary forces acting on a structure or objects that can be removed, such as the weight of books on a shelf.
Structure
A structure is something that is built or constructed, such as a building.
A structure is something that holds or supports a load. For example, a garden shed has four walls that support a roof.
Structures are built for one or more purposes. A garden shed provides a place to keep garden tools dry. A locked shed will also keep the tools safe so they will not be stolen.
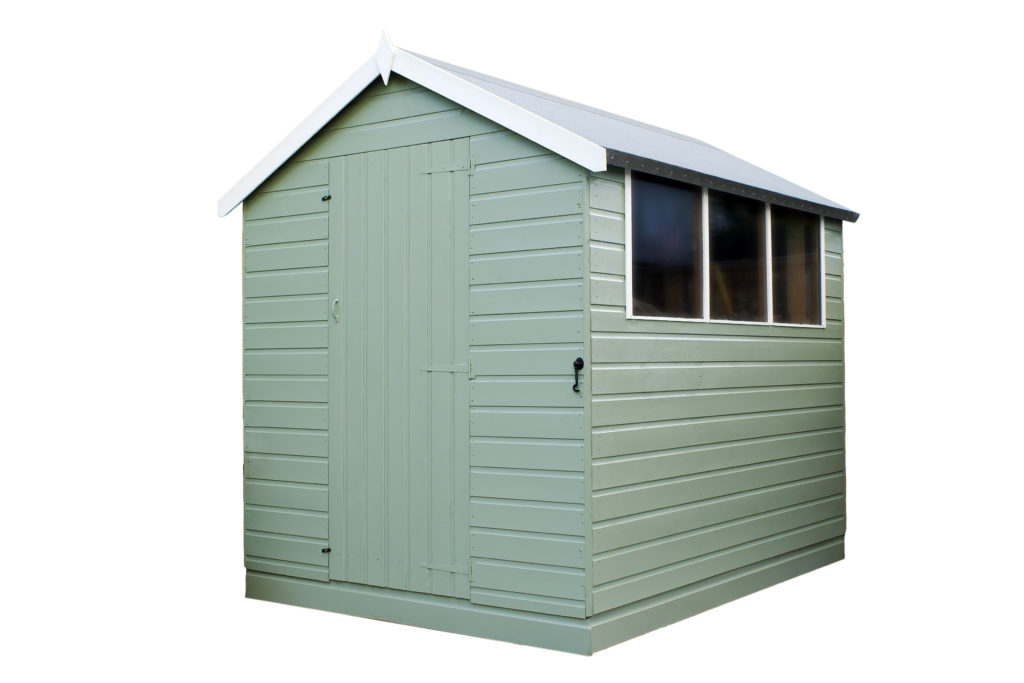

What Types of Forces Act on Structures?
Two types of forces act on structures—internal forces and external forces.
Internal forces are forces that are created from parts of the structure. For example, the roof of a house is heavy and pushes down on the outside walls. The roof is part of the structure of the house. If the walls are not strong enough to hold up the roof, the house will collapse. So the pushing force created by the weight of the roof is an internal force.
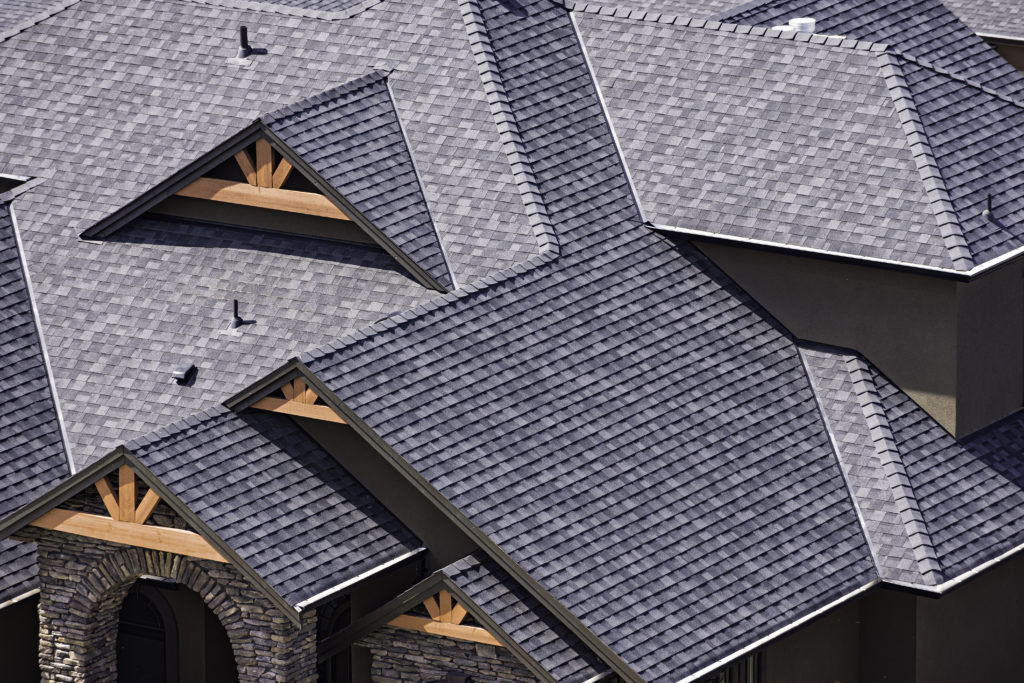

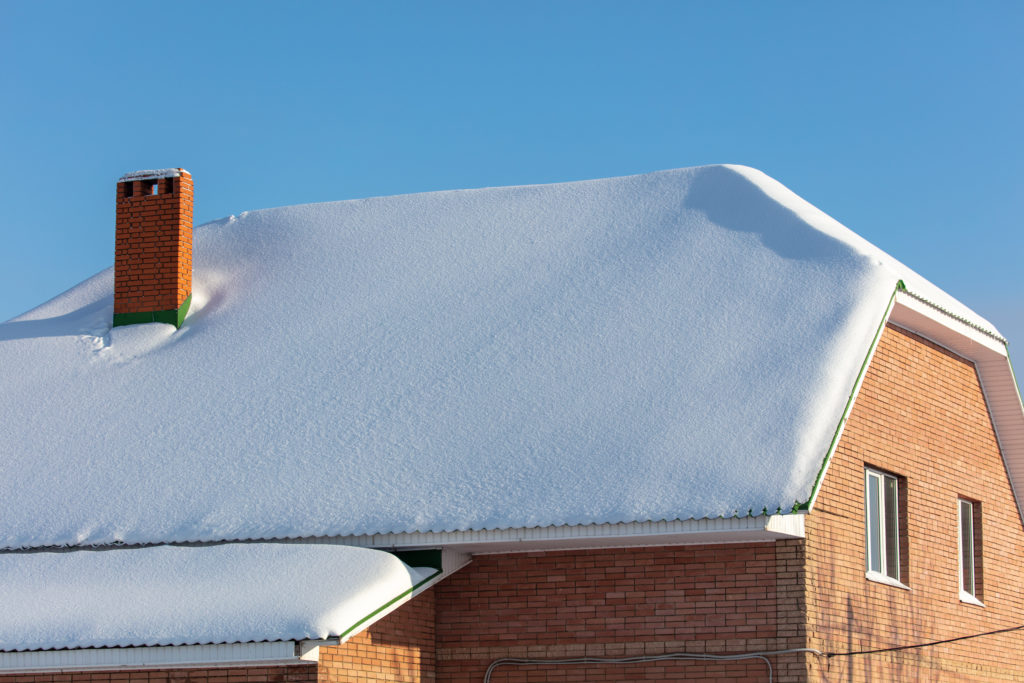
External forces come from things that are not part of the structure. For example, snow will push its weight down on the roof. The walls also have to be strong enough to support the weight of snow on the roof. Because the snow is not part of the structure, snow is an external force.

Two Types of Loads
Loads are forces that act on a structure. All structures need to be strong enough to hold up under the loads placed on them. Loads are divided into two categories—dead loads and live loads.
Dead Load

A dead load is a permanent force acting on a structure. The weight of the materials used to build a structure are part of the dead load. Anything permanently attached to a structure is part of the dead load. Carpet and window planters are dead loads.
Live Load
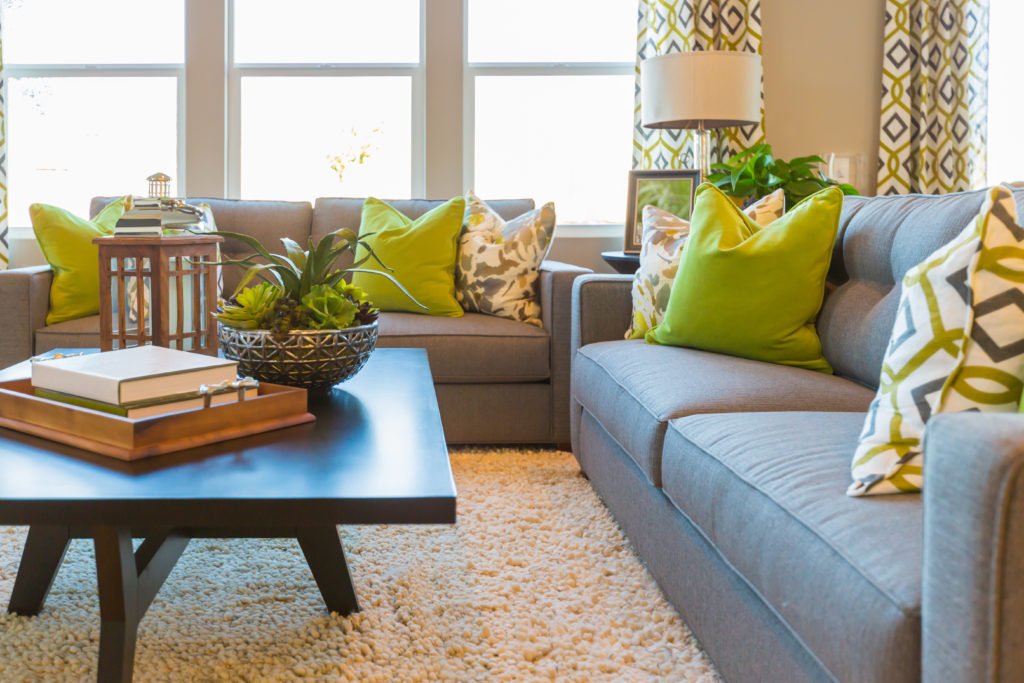


A live load is a temporary force acting on a structure. Objects that carry temporary loads are also part of the live load. Here are some examples:
- Furniture is part of the live load in a house. Furniture can be removed from the house if you move to a new house.
- Snow that builds up on a house roof is a live load. Snow is temporary because it can melt away or be removed.
Show What You Know!
Complete some questions about the reading selection by clicking “Begin Questions” below.